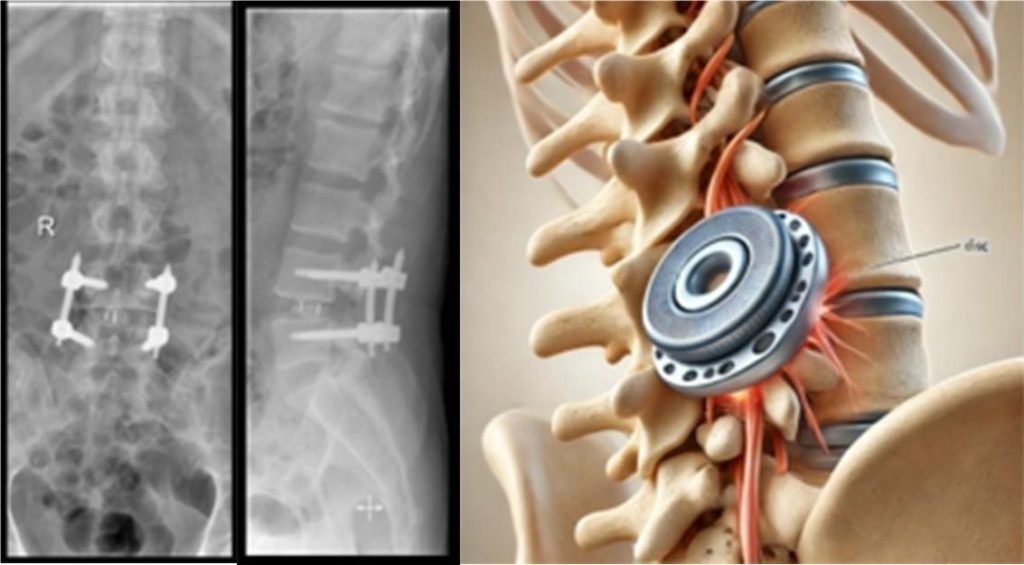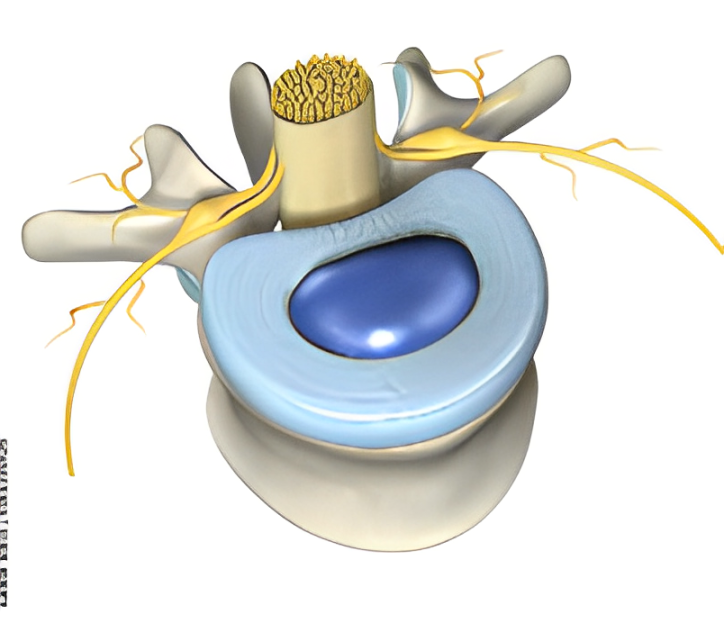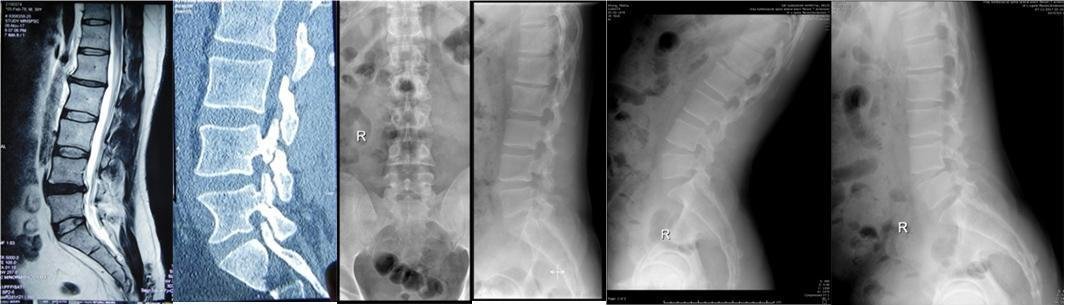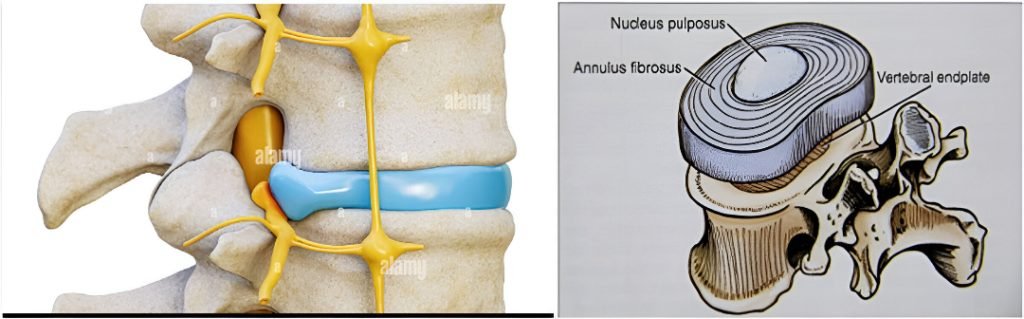
Description
Symptoms:
-
Pain: Typically localized in the affected area of the spine (neck or lower back).
-
Stiffness: Especially after prolonged sitting or standing.
-
Radiating pain: Into the arms or legs, depending on the location of the affected discs.
-
Numbness or tingling: In the extremities.
-
Weakness: Especially in the muscles served by the affected nerves.
Treatments Available
1. Conservative Measures
Including physical therapy, pain management with medications, and lifestyle modifications (e.g., exercise, posture correction).