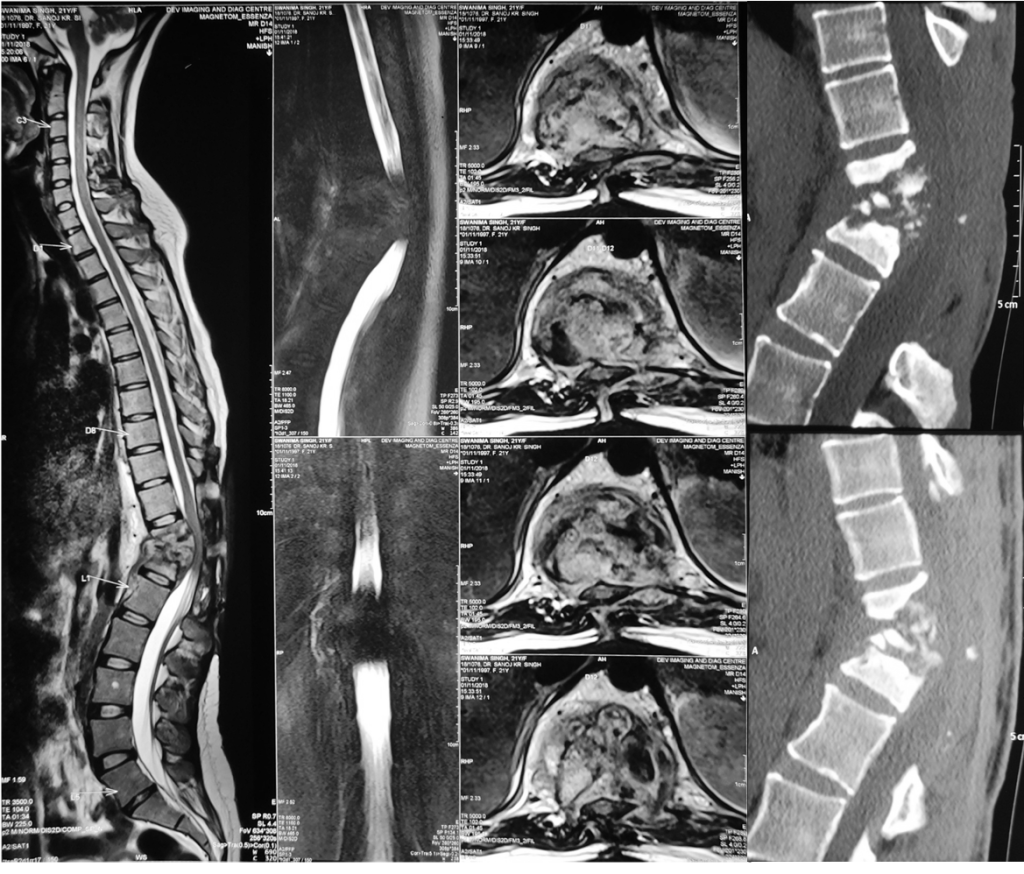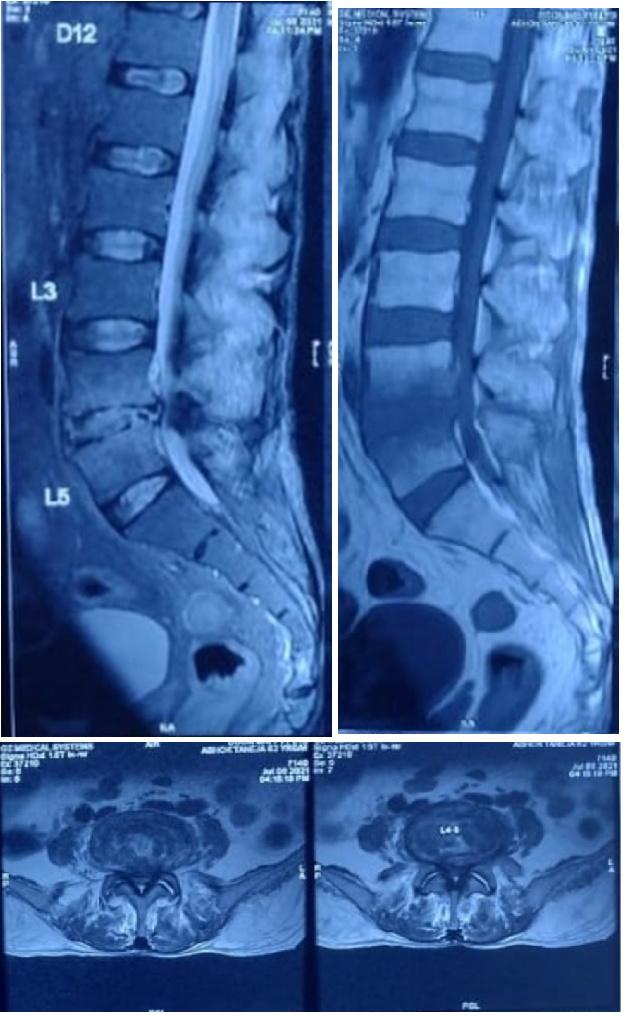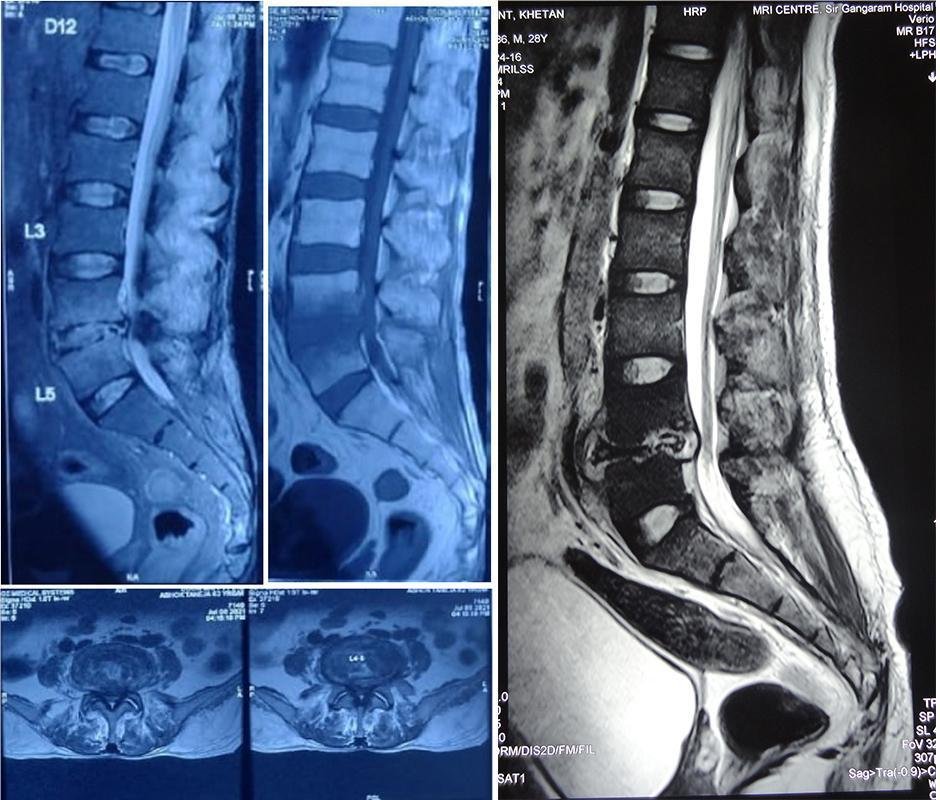
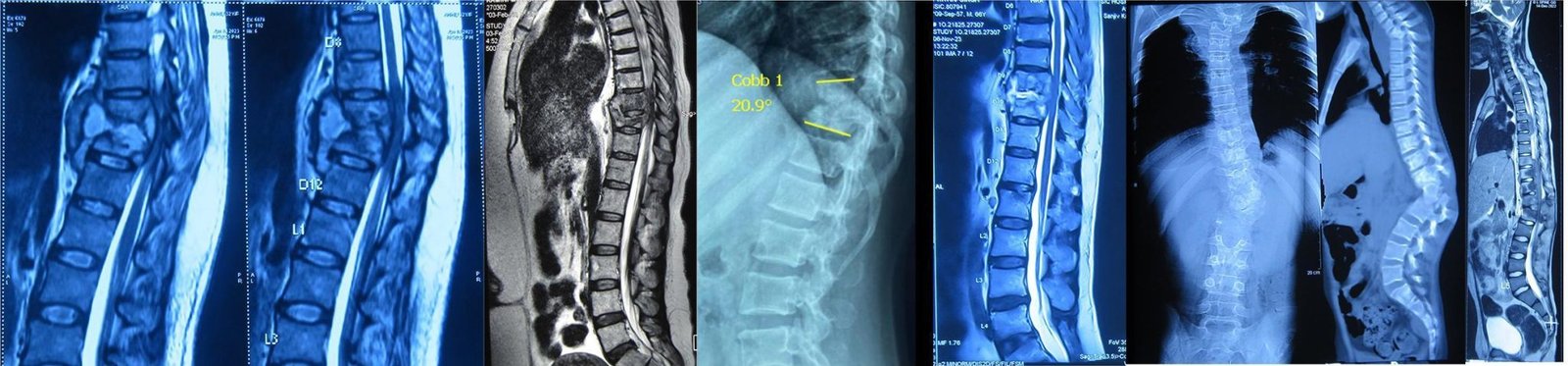
2.Tuberculosis of the Spine (Koch’s Spine)
Koch’s spine, or spinal TB, is a form of tuberculosis affecting the spine. It is common in countries with a high prevalence of TB, like India.
-
Causes: Mycobacterium tuberculosis, often spreading from the lungs.
-
Symptoms: Gradual back pain, fever, weight loss, fatigue, and sometimes spinal deformity.
-
Complications: Can lead to a hunchback deformity (gibbus) and neurological issues.
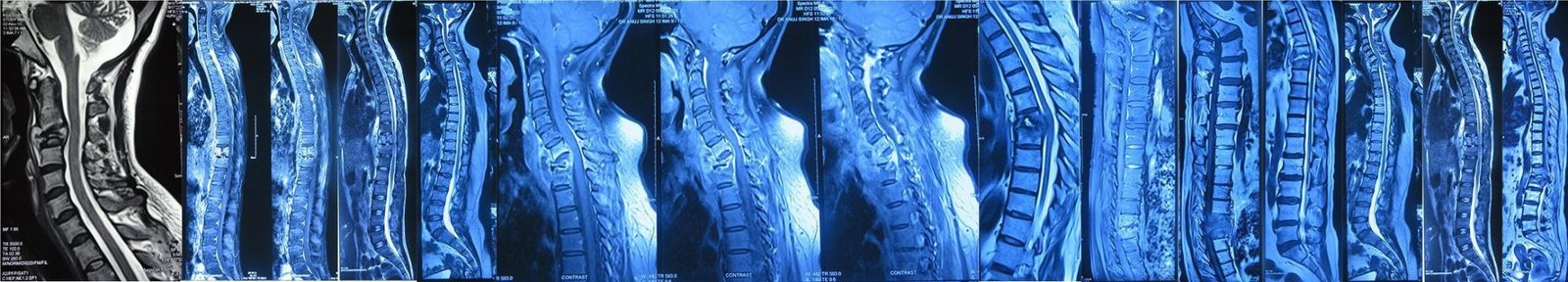

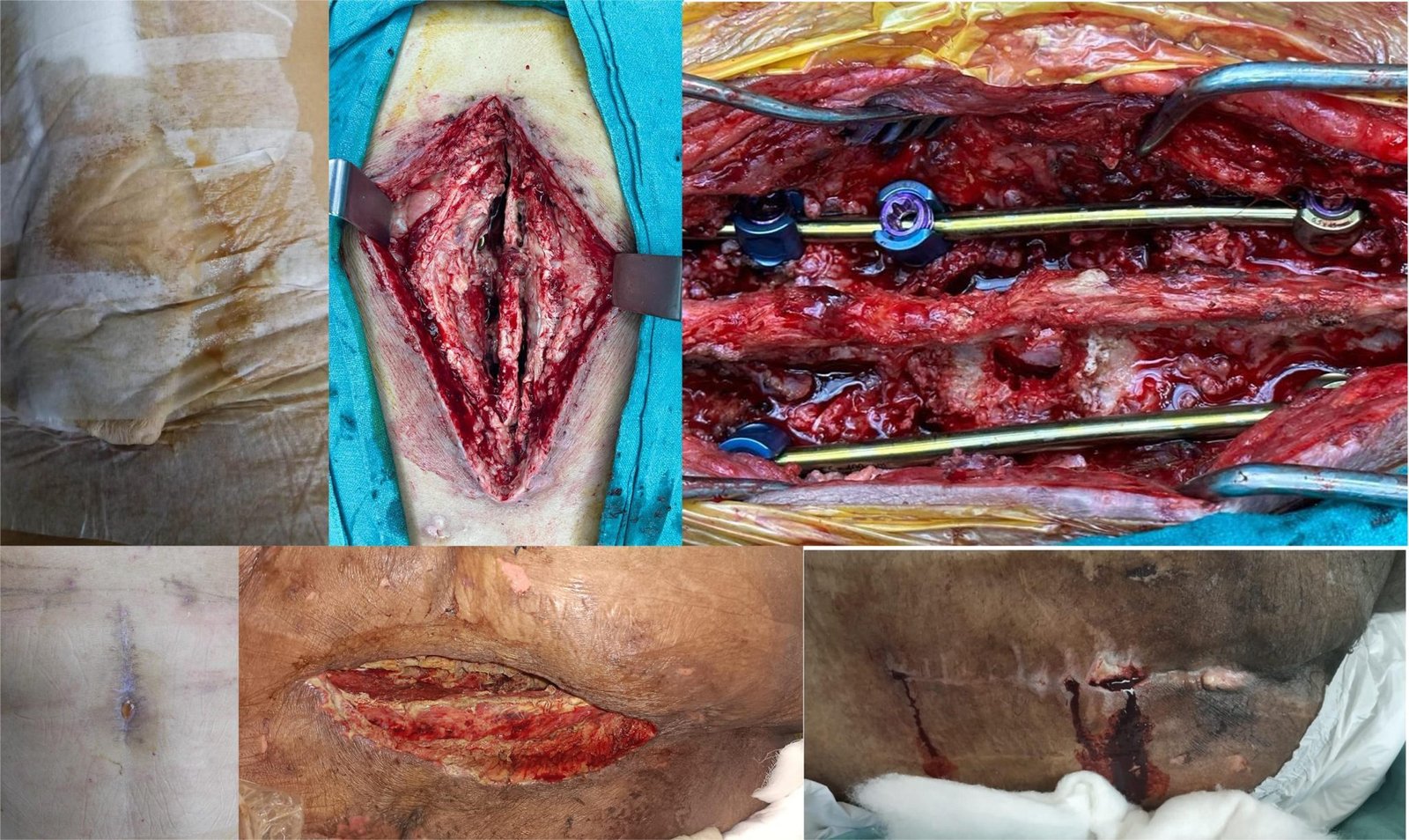
3. Postoperative Spinal Infections
These infections occur after spine surgeries or invasive procedures.
-
Causes: Bacteria introduced during or after surgery.
-
Symptoms: Swelling, redness, fever, and drainage from the surgical site.
-
Risk Factors: Poor hygiene, diabetes, or compromised immunity.
4. Fungal Infections of the Spine
Rare but serious, fungal infections can affect the spine, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
-
Causes: Fungi such as Candida, Aspergillus, or Cryptococcus.
-
Symptoms: Gradual onset of pain, fever, and fatigue.
-
Common in: People with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or long-term steroid use.
5. Pyogenic (Bacterial) Infections
Bacterial infections, such as those caused by Staphylococcus or Streptococcus species, can affect multiple areas of the spine, including bones, discs, and soft tissues.
-
Causes: Bloodstream infections, trauma, or direct spread from nearby sites.
-
Symptoms: Rapid onset of back pain, fever, and swelling.
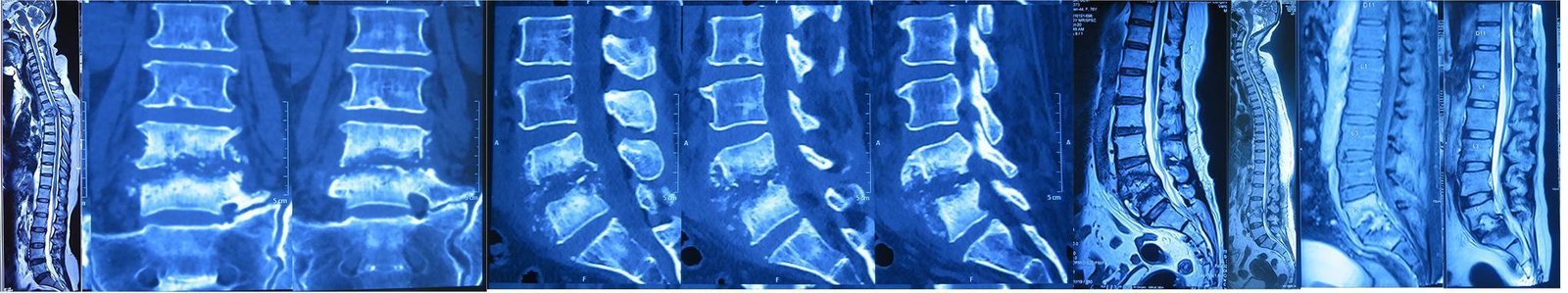
6. Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is an infection of the vertebrae (spinal bones). It can be caused by bacteria or fungi and often spreads to the spine through the bloodstream.
-
Causes: Staphylococcus aureus (common bacteria), fungal infections, or trauma.
-
Symptoms: Severe back pain, fever, chills, and localized tenderness.
-
Common in: People with weakened immune systems, diabetes, or after spine surgeries.
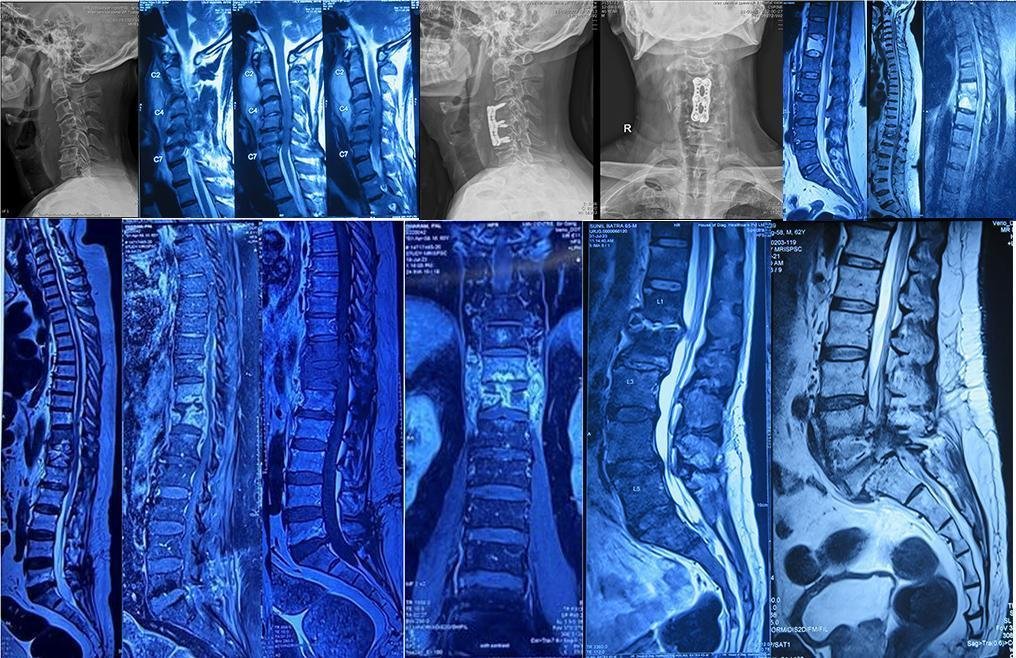
7. Epidural Abscess
An epidural abscess is a collection of pus that forms in the space between the spinal cord and its protective covering (epidural space).
-
Causes: Bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus or post-surgical infections.
-
Symptoms: Severe back pain, fever, neurological symptoms (weakness, numbness), and difficulty walking.
-
Complications: If untreated, it can compress the spinal cord, leading to paralysis.
8. Paraspinal Abscess
This involves the formation of an abscess in the soft tissues around the spine.
-
Causes: Bacteria, tuberculosis, or spread from nearby infections.
-
Symptoms: Pain near the infection site, swelling, and fever.
-
Complications: Can spread to the spine or other parts of the body.
Symptoms of Spinal Infections
Symptoms may vary but often include:
-
Severe back pain that worsens with activity
-
Fever, chills, and night sweats
-
Swelling or redness over the spine
-
Fatigue and unexplained weight loss
-
Difficulty moving or stiffness in the back
-
Neurological symptoms, such as numbness, weakness, or difficulty walking (if nerves are affected)
How Are Spinal Infections Diagnosed?
Dr. Shankar Acharya, an experienced spine specialist, uses advanced diagnostic methods, including:
-
Medical History and Physical Examination: Identifying symptoms and potential risk factors.
-
Blood Tests: Checking for signs of infection, such as high white blood cell counts or inflammatory markers.
-
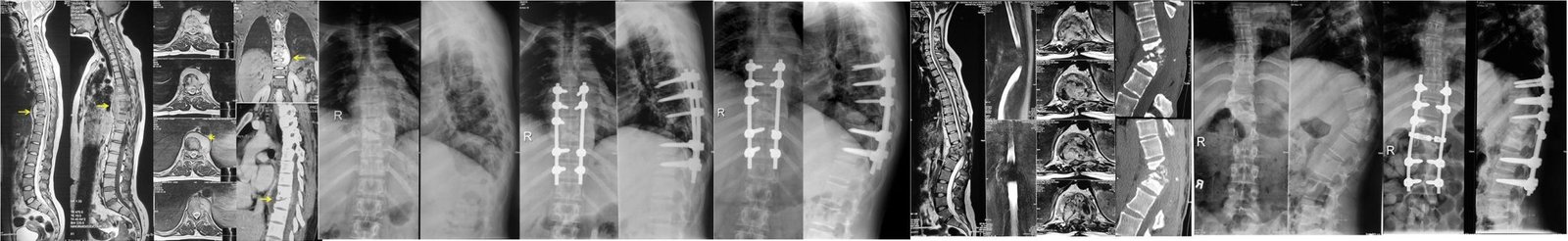
Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to detect infections or damage in the spine.
-
Biopsy: Collecting tissue samples from the infected area to identify the exact cause.
Treatment Options for Spinal Infections
Treatment depends on the type and severity of the infection. Common approaches include:
1. Medications
-
Antibiotics or Antifungal Medicines: To eliminate the infection.
-
Anti-TB Drugs: For treating Koch’s spine.
2.Bed Rest: Reducing movement helps the spine heal.
3. Bracing: A brace may be recommended to support the spine and reduce pain.
4. Surgery: For severe cases, surgery may be needed to remove infected tissue, stabilize the spine, or relieve nerve pressure. Dr. Shankar Acharya is highly skilled in performing minimally invasive and advanced spinal surgeries.
Preventing Spinal Infections
-
Maintain Hygiene: Good hygiene reduces the risk of infections.
-
Seek Early Treatment: Address symptoms like fever or persistent back pain promptly.
-
Healthy Lifestyle: Eating nutritious food and avoiding smoking or alcohol helps strengthen the immune system.
Why Early Diagnosis is Important ?
Spinal infections can lead to severe complications, such as spinal deformity, nerve damage, or paralysis, if untreated. Consulting a specialist like Dr. Shankar Acharya ensures timely diagnosis and effective treatment, tailored to the type of infection.